How Should Different Caster Wheel Types Be Evaluated for Practical Use?
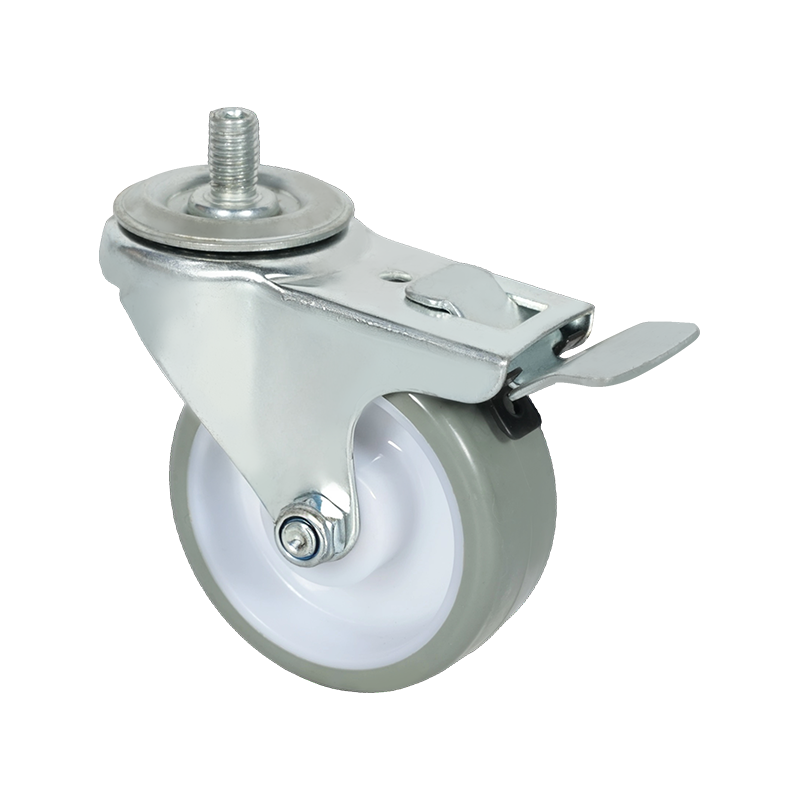
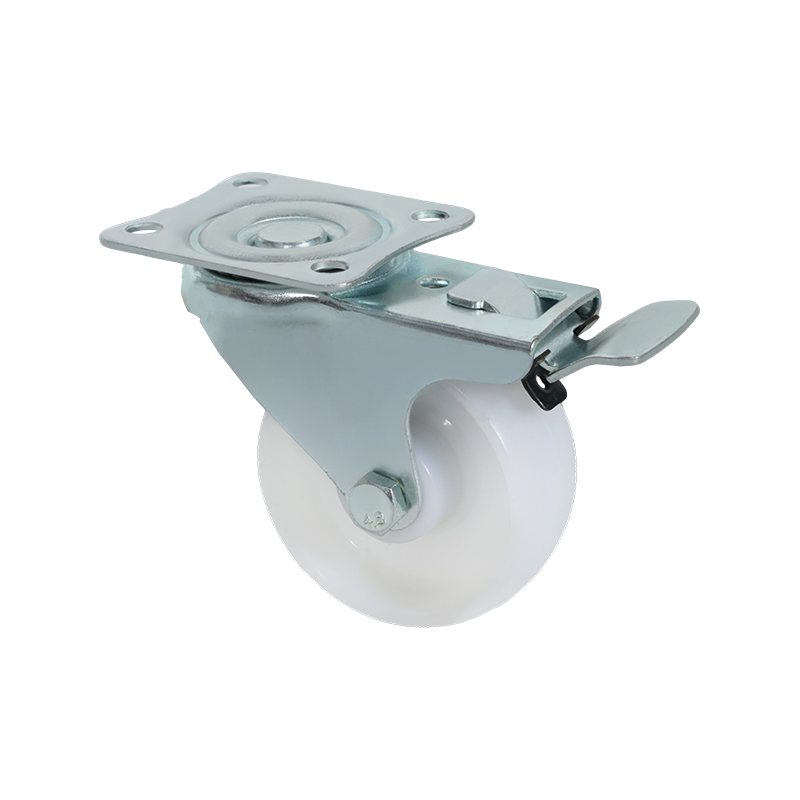
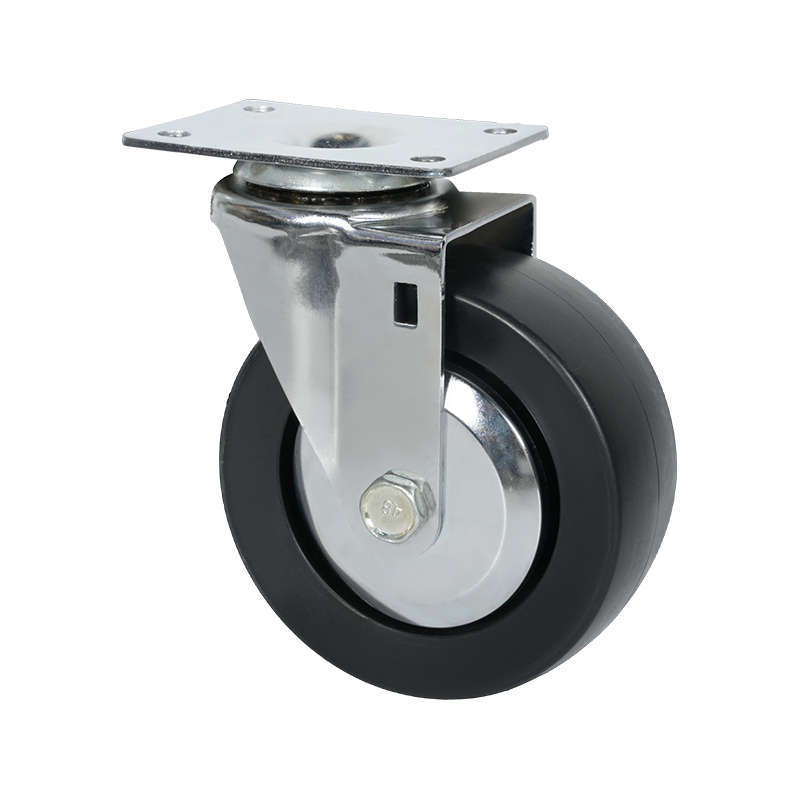
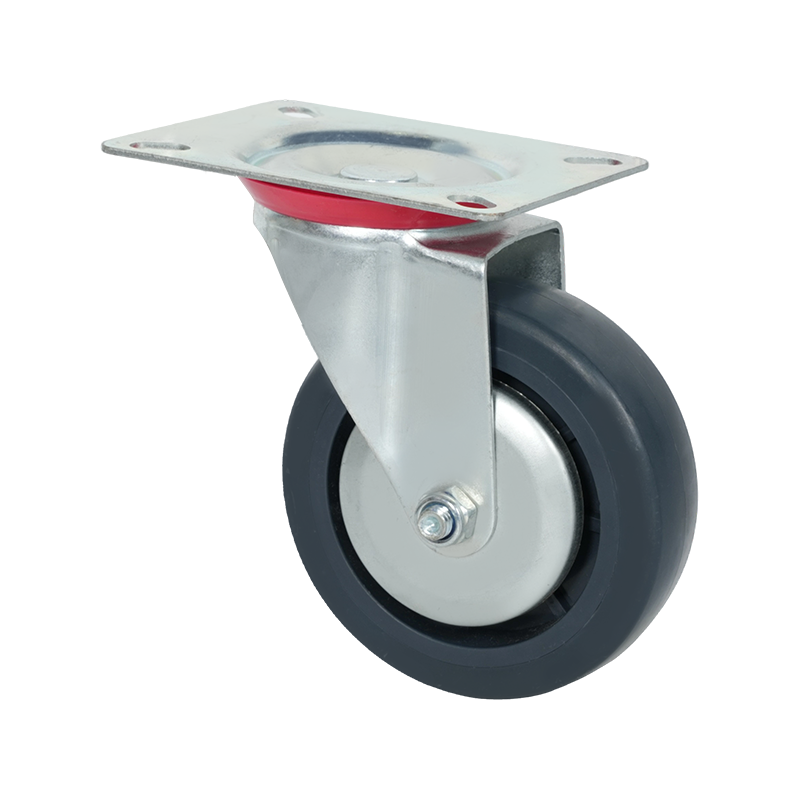
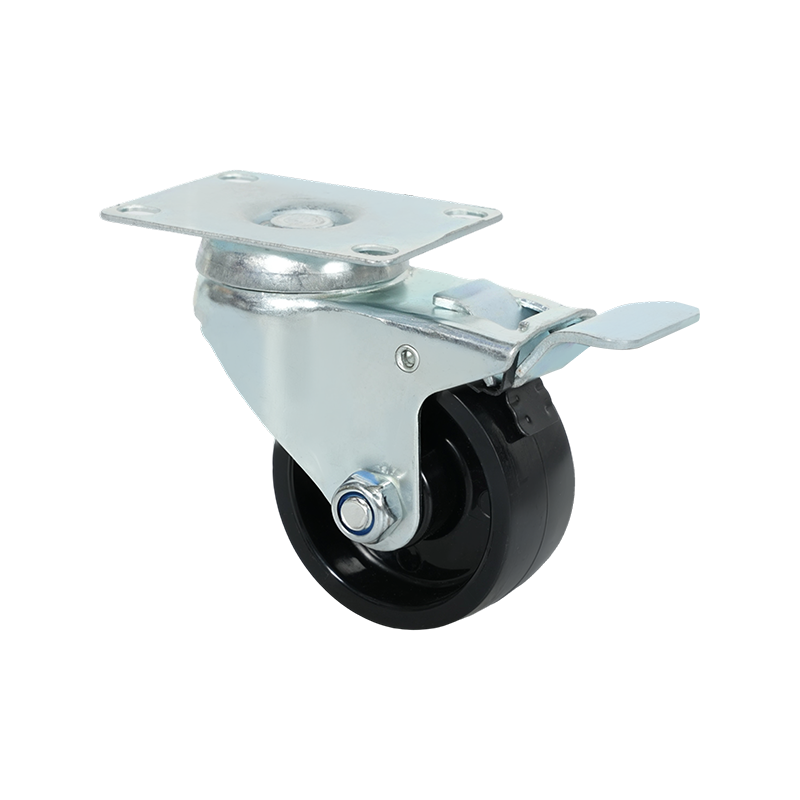
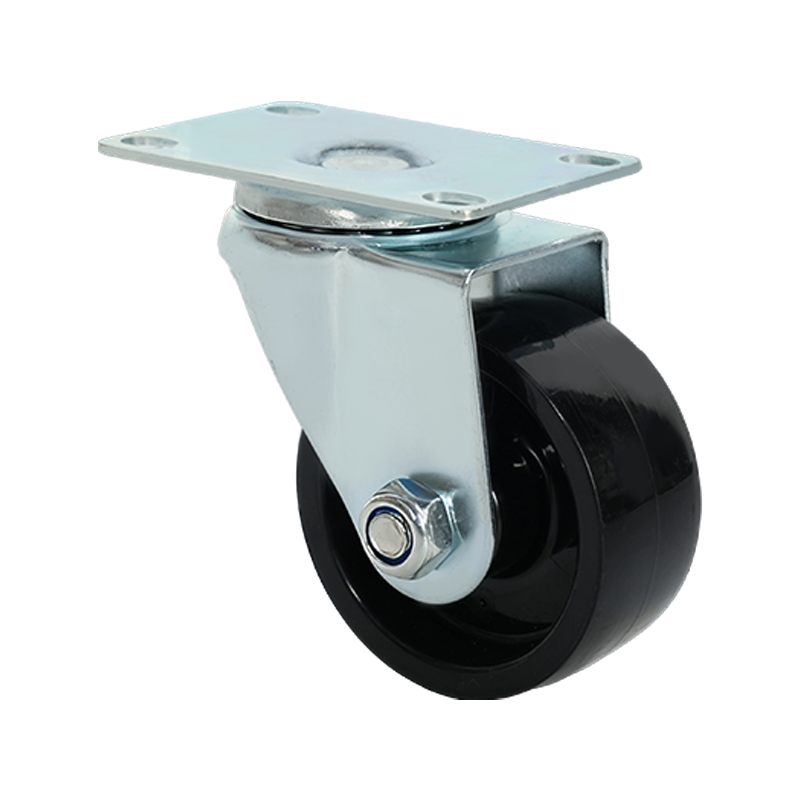
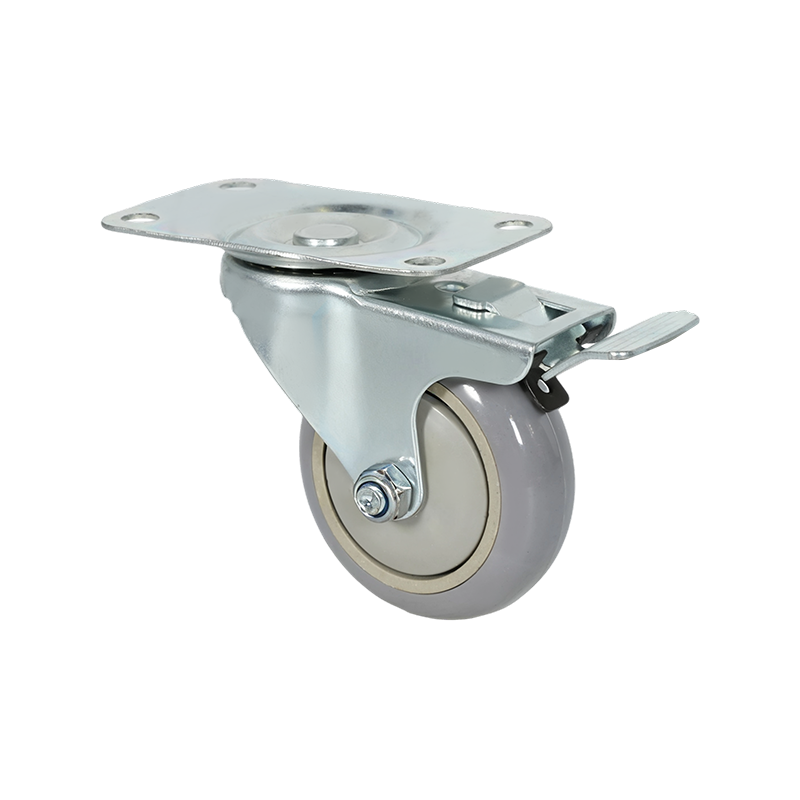
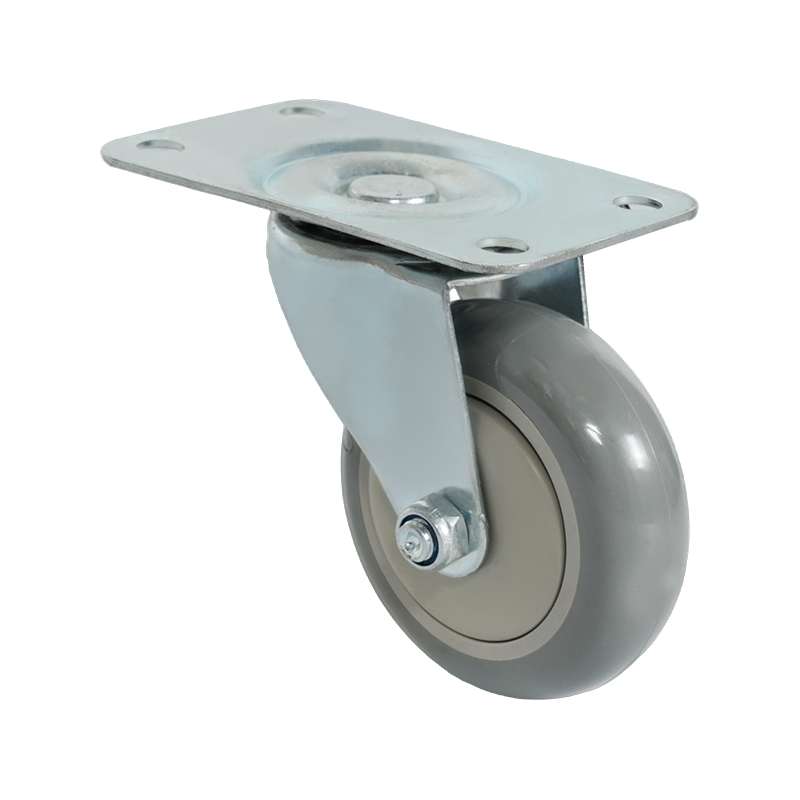
Swivel caster wheels are widely used in applications where maneuverability is a primary requirement. Unlike rigid casters, swivel casters rotate 360 degrees around a vertical axis, allowing equipment to change direction smoothly without repositioning. This feature makes them suitable for carts, trolleys, medical equipment, industrial racks, and mobile workstations where frequent directional changes occur.
Structurally, a swivel caster consists of a wheel, a fork (also known as a yoke), and a swivel bearing or raceway. The bearing allows the caster to rotate freely under load. Depending on the design, swivel casters may also include brakes, which can lock either the wheel rotation, the swivel motion, or both. This adds stability when stationary positioning is required.
Swivel caster wheels are available in a wide range of materials, such as polyurethane, rubber, nylon, or cast iron. Each material choice affects rolling resistance, floor protection, noise levels, and load capacity. For example, softer wheels tend to reduce vibration and floor damage, while harder wheels generally support higher loads and roll more easily on smooth surfaces.
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Rotation |
360-degree swivel movement |
|
Typical Mounting |
Plate-mounted or stem-mounted |
|
Wheel Materials |
Rubber, polyurethane, nylon, cast iron |
|
Common Applications |
Carts, equipment stands, hospital beds |
|
Optional Functions |
Directional locks, total brakes |
Key Characteristics of Screw-Mounted Caster Wheels
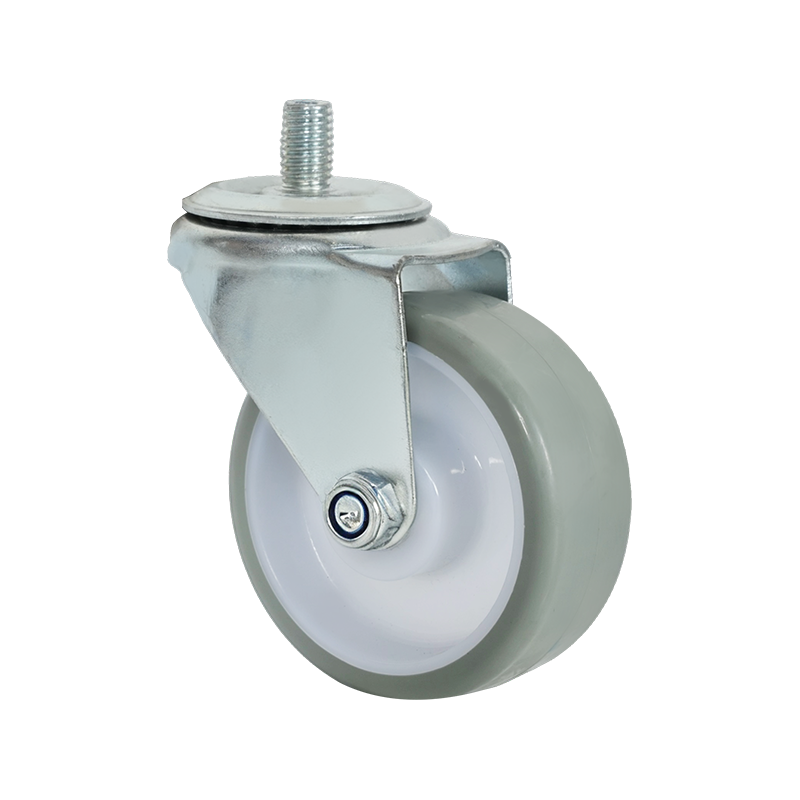
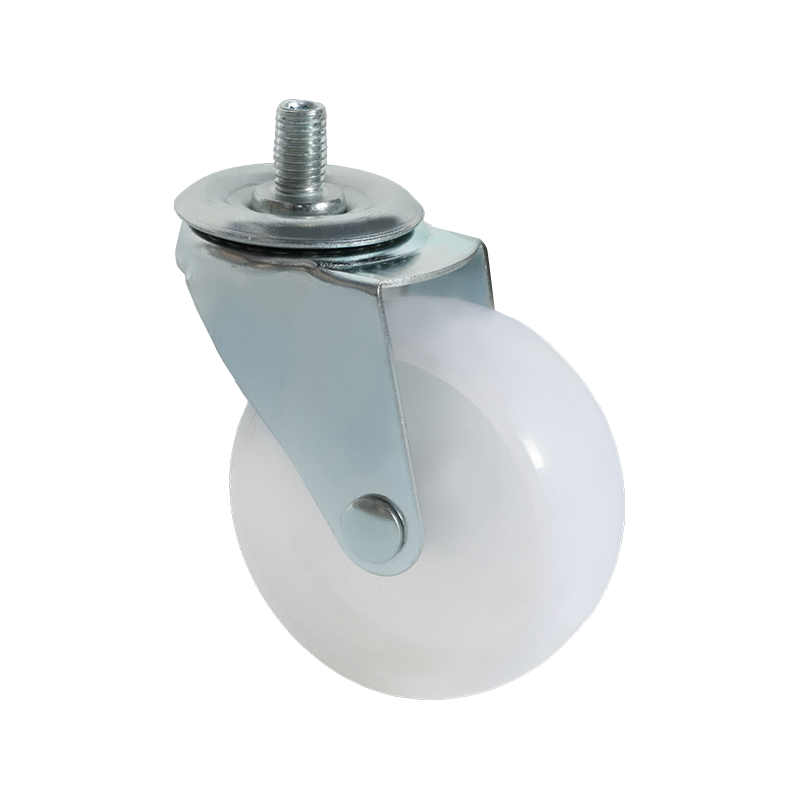
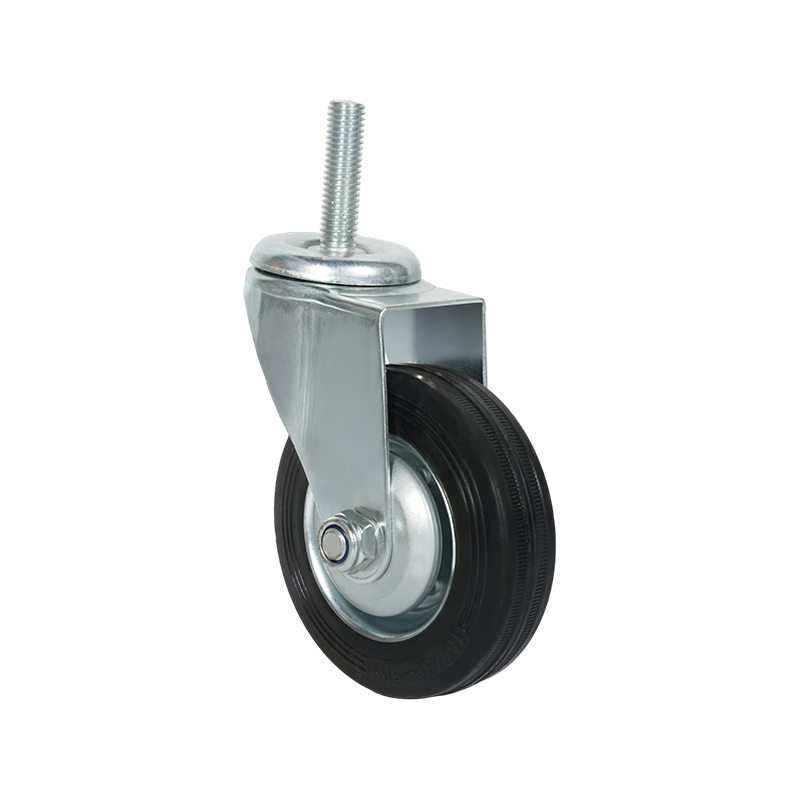
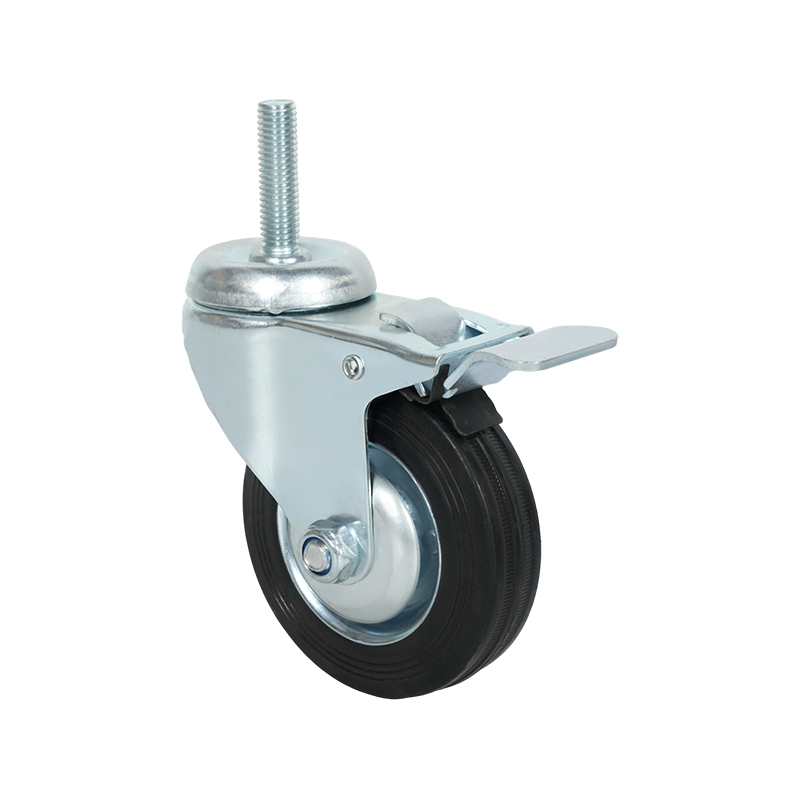
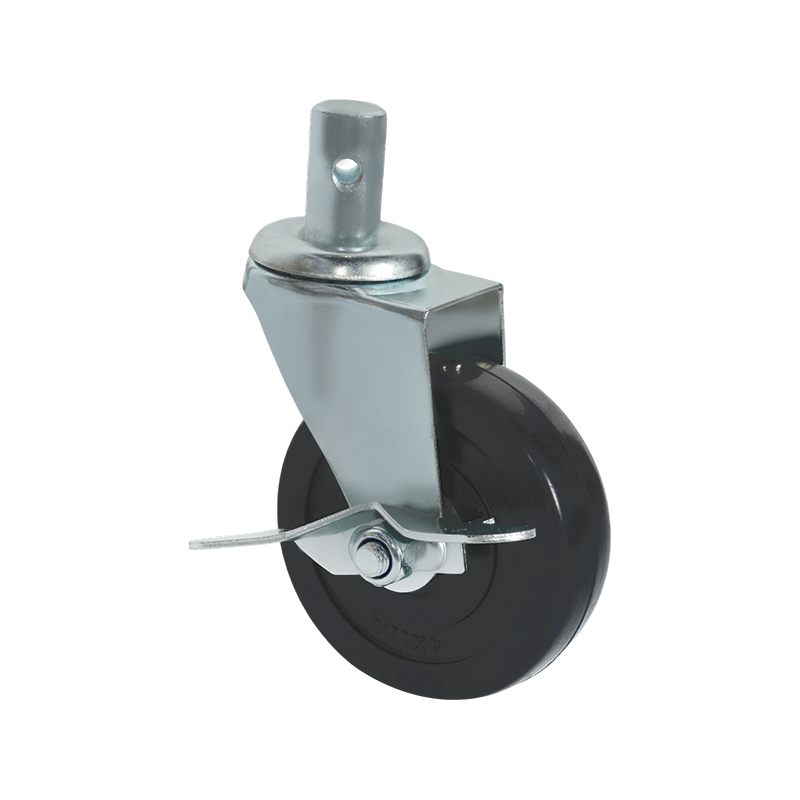
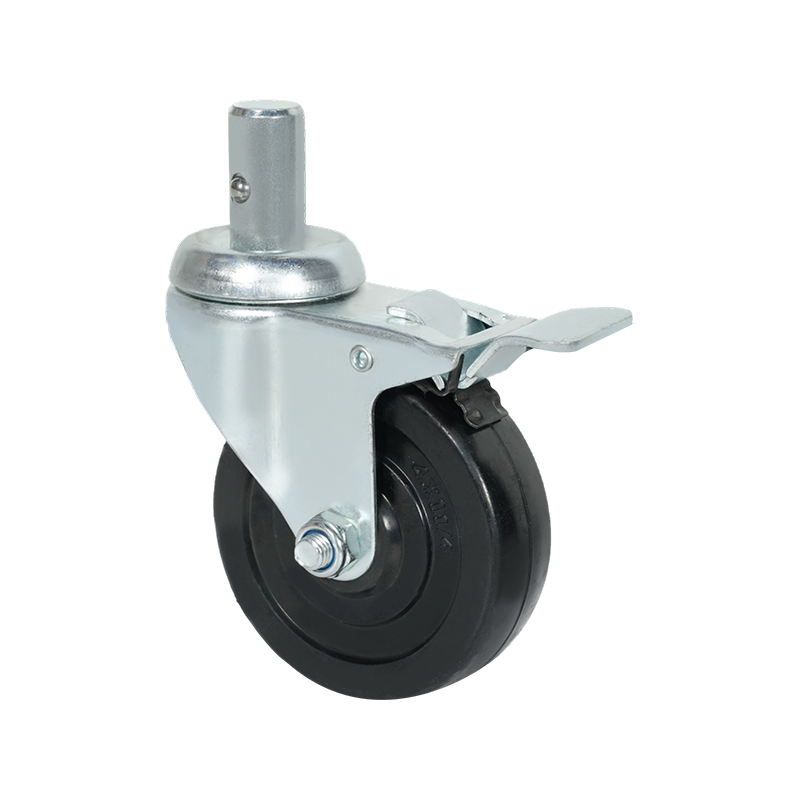
Screw-mounted caster wheels are distinguished primarily by their installation method. Instead of using a top plate with multiple bolts, these casters are fixed using a single threaded stem or screw that inserts directly into the equipment frame. This mounting style is common in lighter-duty applications where simplicity and compactness are important.
One notable characteristic of screw-mounted casters is ease of installation. With fewer components required, mounting and replacement can often be completed quickly using basic tools. This makes them suitable for office furniture, display stands, small storage racks, and household carts. In addition, the reduced mounting footprint allows them to be used in designs where space constraints limit the use of plate-mounted alternatives.
From a structural standpoint, screw-mounted casters generally support lower load capacities compared with plate-mounted or heavy-duty casters. The load is concentrated through the threaded stem, which places greater stress on the mounting point. As a result, these casters are typically selected for light to moderate loads and for applications where movement is intermittent rather than continuous.
Screw-mounted caster wheels are available in both swivel and rigid configurations, and some models include braking mechanisms. Wheel materials often focus on floor-friendly options, such as thermoplastic rubber or soft polyurethane, to minimize surface damage in indoor environments. While they may not be suitable for industrial transport tasks, their balance of convenience, compact design, and sufficient performance makes them a practical choice for many light-duty uses.
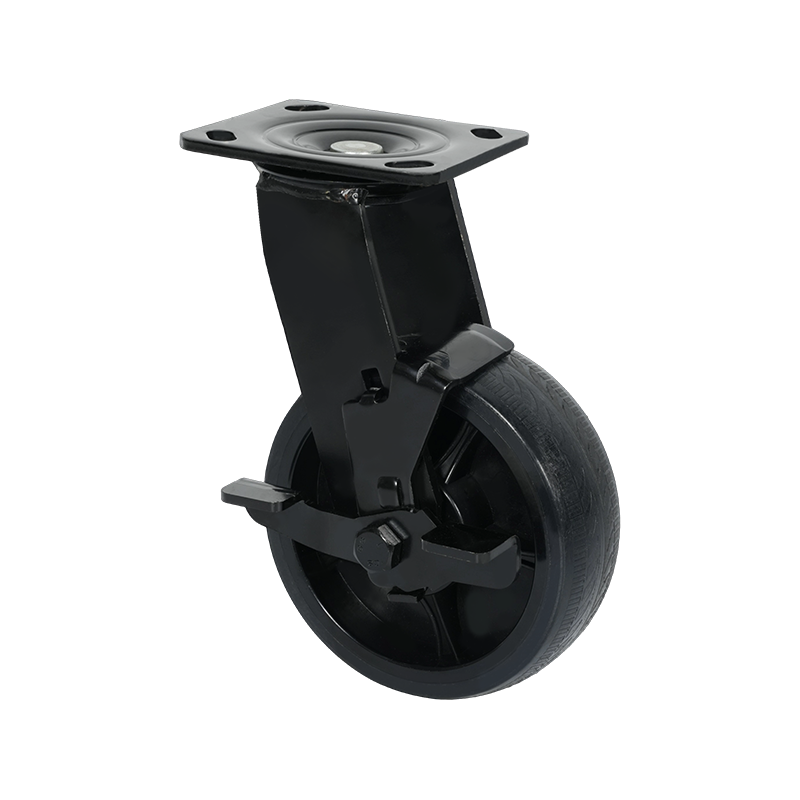
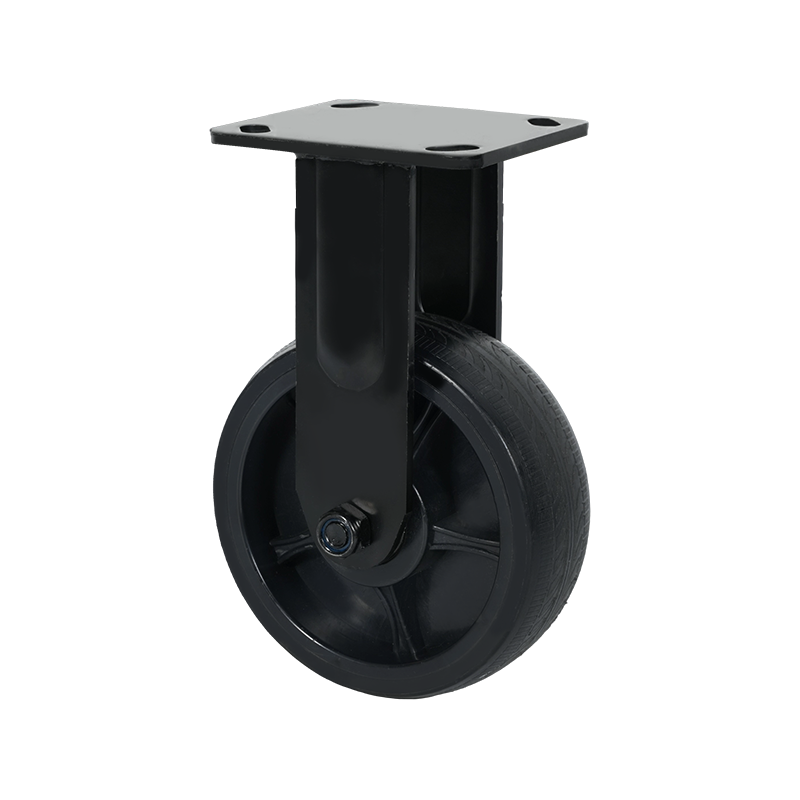
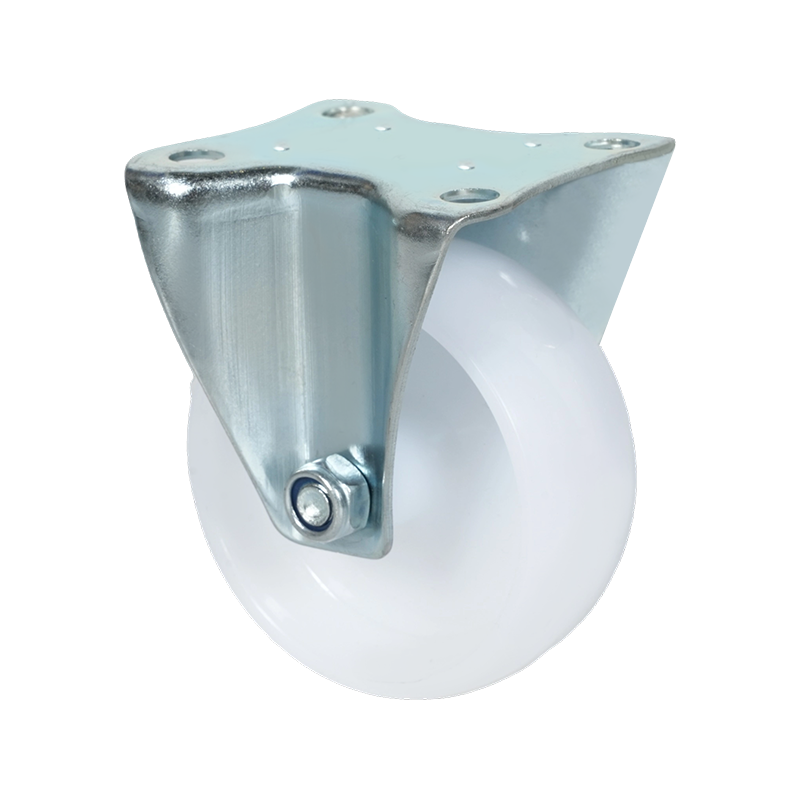
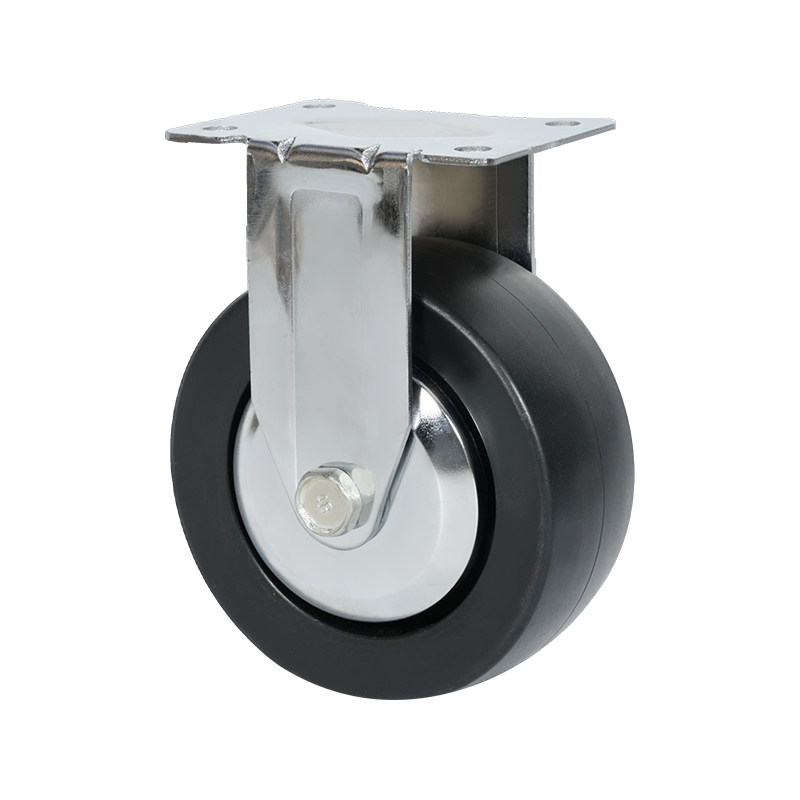
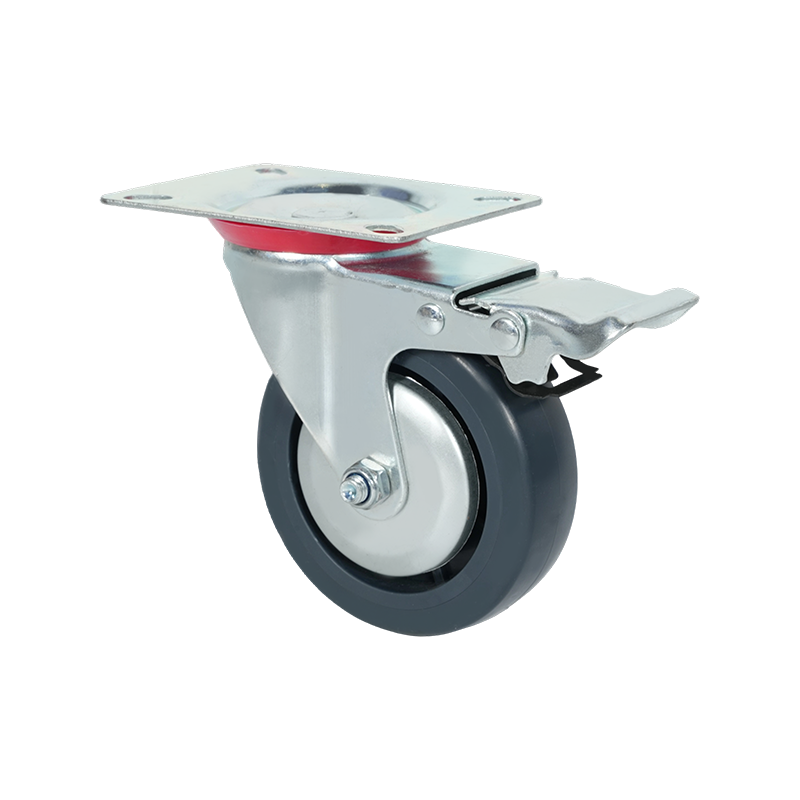
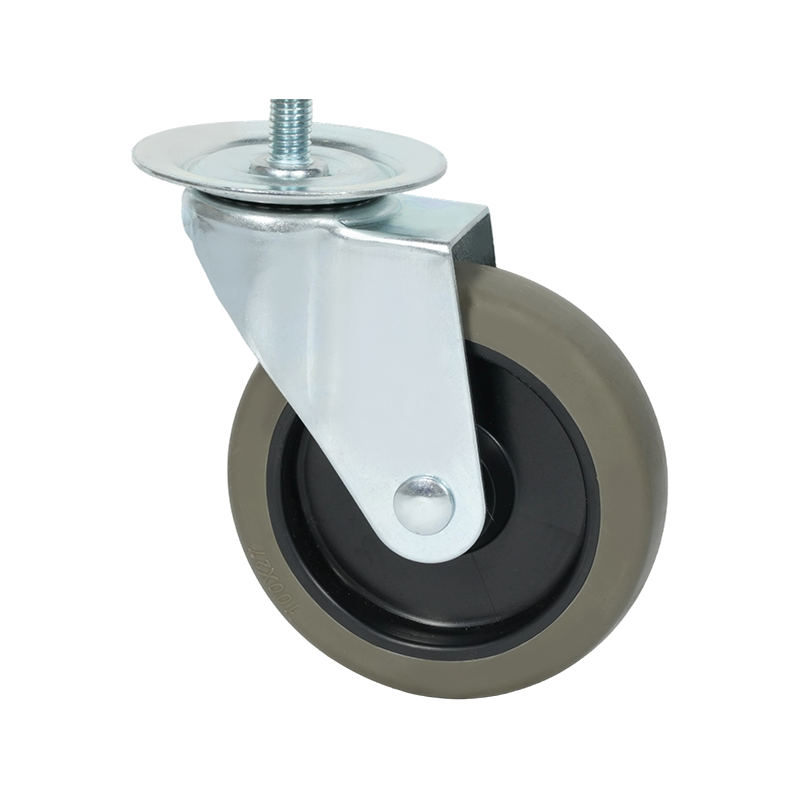
Common Specifications Available for Heavy-Duty Caster Wheels
Heavy-duty caster wheels are engineered to handle substantial loads, continuous movement, and demanding operating conditions. Their specifications are designed to ensure stability, durability, and consistent performance in industrial environments such as factories, warehouses, and logistics centers.
One of the primary specifications for heavy-duty casters is load capacity. Individual caster ratings can range from several hundred kilograms to well over a ton per wheel, depending on wheel diameter, material, and bearing type. Larger wheel diameters are often preferred, as they distribute weight more effectively and roll more easily over uneven surfaces.
Mounting style is another key specification. Heavy-duty casters are commonly plate-mounted using thick steel top plates with reinforced bolt holes. This spreads the load across a wider area and reduces stress on the equipment frame. Stem-mounted options exist but are less common in high-load applications.
Wheel material selection plays a significant role in performance. Common options include forged steel, cast iron, high-capacity polyurethane, and nylon. Metal wheels offer high load ratings and resistance to heat, while polyurethane-coated wheels provide a balance between load capacity and floor protection. Bearing types, such as roller bearings, ball bearings, or tapered bearings, further influence rolling efficiency and service life.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体